【Information Theory, Pattern Recognition, and Neural Networks】Introduction
前置知识
- 二项分布
- Stirling(斯特林)近似
主要内容
- (7,4)汉明码
- 香农有噪信道编码定理
Introduction to Information Theory
The fundamental problem of communication is that of reproducing at one point either exactly or approximately a message selected at another point. (Claude Shannon, 1948)
有噪信道下的“完美”通信
- Some examples of noisy communication channels

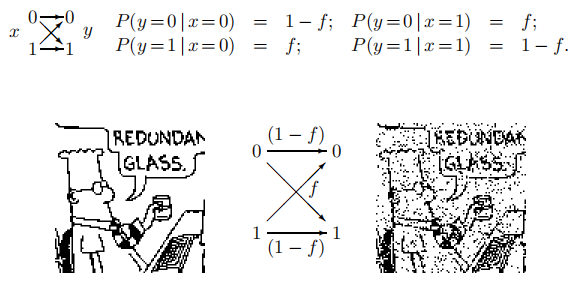
- Binary symmetric channel, BSC (二进制对称信道)
- Sol.
- Physical solution(如使用更多可靠元器件/真空减少干扰/更高信号功率或降低热噪)
- System solution
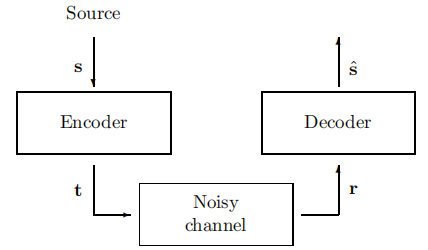
Only cost being a computational requirement at the encoder and decoder.
- 信息论关注:“能够达到的最佳纠错性能是多少?”
编码理论关注:“如何创建实用的编译码系统?”
Error-correcting codes for the binary symmetric channel
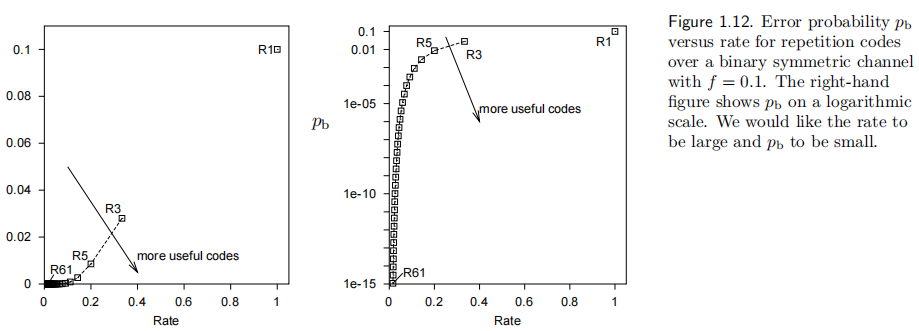
Repetition codes (重复码)
(7, 4) Hamming code (汉明码)
What performance can the best codes achieve?
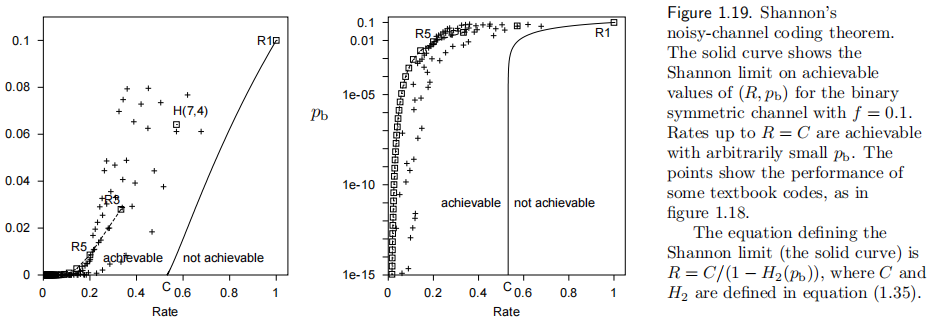
- 对于噪声水平
的 BSC 信道根据信道容量公式 。例如对于错误率 0.1 的磁盘,如果采用类似重复码架构,可以通过约 60 个这样的磁盘构造出 的磁盘,而 Shannon 的结论说明可以用 2 个磁盘( )即可做到。
当然,这里的比喻不完全正确,因为 Shannon 通过研究分组长度递增的分组码序列才证明了噪声信道编码定理